- 74 Mount Street, Heidelberg, VIC, 3084
- Monday to Friday: 9am to 5pm
Hearing Tests For Kids
-
DWM Audiology > Our Services > Hearing Tests For Kids
Hearing Tests For Children
Normal hearing and normal auditory processing abilities enable children to develop their language, communication and social skills. This allows children to engage with the world around them and promotes educational achievement.
If you have concerns about your baby or child’s hearing, have them tested by an experienced audiologist. At DWM Audiology, we offer hearing assessments for all children aged from 9 months.
We provide a range of hearing tests designed to give you an accurate understanding of your child’s hearing levels and ear health. A 30 minute appointment is arranged for all children 18 years and younger. The tests used will depend on your child’s age and, in children aged 3 years and up, their ability to concentrate and listen. Ideally, arrange the appointment at a time of day when your child will be most alert and receptive.
Medicare rebates for your child’s hearing assessment are available with a GP, ENT Specialist or Neurologist referral.
Hearing From Birth To Kindergarten
A hearing screening test is now included in the routine assessments provided to babies in the first few days of life. These tests are designed to detect a permanent hearing loss in a child. A pass in these test results at birth indicates that the child has sufficient hearing for normal speech and language development.
Babies and children are highly susceptible to temporary or fluctuating hearing loss. A hearing loss in the early years of childhood can have a significant impact on the development of language and social skills. These skills established in preschool years are the foundation for future learning at school.
Indications that your baby can hear
Newborn to eight weeks
Your baby is startled or widens their eyes at sudden noises nearby or is woken or stirred from sleep by noise
Eight weeks to four months
Your baby is looking towards the direction of sound and they may quieten while listening
Six to 12 months
Your baby is starting to turn their head towards known voices or sounds and is starting to babble
12 to 18 months
Your toddler knows the names of their favourite toys and is beginning to imitate simple words and sounds
18 to 24 months
Your toddler has a small vocabulary of single words and can understand simple directions such as "Give mummy the ball"
Two-and-a-half to 4 years
Your child has clear speech with a good vocabulary
Temporary mild hearing loss in children
There are some common causes of temporary hearing loss in children, including:
- A build-up of wax in the ear canal
- Reduced middle ear ventilation due to Eustachian tube blockage, caused by congestion. The Eustachian tube is a passageway that connects the ear, nose, and throat.
- Middle ear fluid
- Middle ear infection (otitis media)
Hearing in School-Age Children
Hearing difficulties in school-age children are known to have a significant impact on their social, behavioural and academic growth.
Indications of hearing problems in older children include the child:
- Not responding when called
- Talking too loudly
- Watching the television with the volume turned up loudly
- Pronouncing words incorrectly
- Appearing inattentive and prone to daydreaming
As well as diagnostic hearing assessments for children, DWM Audiology can support your child with abnormal sound intolerance by providing Hyperacusis and Misophonia evaluation and management.
Central Auditory Processing Disorder (CAPD)
Central Auditory Processing describes the skills used by the brain to extract meaningful information from sound. Efficient processing of auditory information is important for children to be successful in learning and communication.
A Central Auditory Processing Disorder (CAPD) can lead to difficulties with educational achievement, social development and educational well-being. We can provide recommendations of clinics who carry out CAPD testing.
Hyperacusis and Misophonia
Hyperacusis is an abnormal sound sensitivity characterised by an intolerance of certain everyday sounds. These are typically loud/impact sounds, multiple sounds, unexpected sounds and sounds close to the ears. Children with hyperacusis experience a heightened sense of volume and physical discomfort to these sounds that other children can tolerate. Hyperacusis develops when those sounds are subconsciously evaluated in the primeval parts of the brain as threatening. This may be due to a belief that those sounds are potentially damaging to the ear/hearing/tinnitus or fear they may cause pain/discomfort, or trauma associations. Hyperacusis can develop in children with high anxiety levels.
Misophonia is a strongly aversive response to specific sound triggers, most commonly eating/sniffing/breathing sounds made by other people. Misophonia often stems from a specific instance in childhood or teenage years where a sound made by a family member elicited a strongly negative reaction of irritation and/or disgust.
Misophonia can lead to hyperacusis.
Neurodivergence: Research has shown that people with autism, ADHD (both inattentive and/or hyperactive) and sensory processing disorders have an increased risk of developing misophonia in childhood. In children with autism, the risk of misophonia development can be enhanced by processing difficulties filtering out unimportant sounds, being overwhelmed by multiple sounds heard simultaneously and difficulty with emotional regulation. In children with ADHD, the risk of misophonia development can be enhanced by focusing difficulties and strong levels of distraction when multiple sounds are heard simultaneously.
Hearing Tests For Children In Melbourne
DWM Audiology offers hearing assessments for children aged 9 months+. Our well known and highly regarded clinic offers extensive experience in hearing assessment and misophonia/hyperacusis evaluation and therapy.
Book an appointment with our expert audiologists today to discuss any hearing concerns you may have for your child. Give us a call or complete the form below.
FAQs
When should children have hearing tests?
Arrange a hearing test if you have any concerns or doubts about your baby or child’s hearing.
Babies and children are highly susceptible to temporary or fluctuating hearing loss, associated with middle ear fluid or middle ear infections. This can have a significant effect on the development of their language and communication skills.
Does my toddler have hearing issues?
Delayed or absent speech development is the most important clue indicating a possible hearing loss in a very young child.
Other signs:
- Your child seems to hear well at times and not respond at other times
- Your child appears inattentive
- Your child starts to speak more loudly than usual
- Your child looks at you intently when you are speaking – they may be depending on visual cues
What can cause a child to lose their hearing?
Common causes of temporary hearing loss in children include:
- Build-up of wax in the ear canal
- Reduced middle ear ventilation due to Eustachian tube blockage, caused by congestion. The Eustachian tube is a passageway that connects the ear, nose, and throat.
- Middle ear fluid
- Middle ear infection (otitis media)
A newborn hearing screening program will detect a permanent congenital hearing loss.
Some genetic hearing losses can develop progressively after birth. Conditions that may cause permanent acquired hearing loss in children include ototoxic medications, encephalitis, mumps, measles, meningitis, large vestibular aqueduct, head injury, sudden onset hearing loss and noise exposure.
How can I get my child’s hearing tested?
We offer hearing assessments for all children aged from 9 months.
What happens if my child fails their hearing test?
Sometimes babies fail their hearing test because of temporary causes such as blockages or fluid in the ear, which can be treated.
Hearing loss is measured by degrees: mild, moderate, severe or profound. Because there are so many different kinds of hearing loss, and so many causes for hearing loss, the appropriate treatments and interventions for your child will depend on the circumstances. We can provide expert, evidence-based advice with regards to appropriate intervention.
Book an Appointment
Our Services

Hearing Tests for Adults
A reduced capacity to communicate has a significant impact on relationships, career opportunities, social connection, independent living and quality of life.
Read More
Do I Need A Hearing Aid?
We carry out a range of hearing tests that help determine whether you need a hearing aid.
Read More
Choosing Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are available in three styles; BTE, RIC or are fully contained in the ear.
Read More
Getting Used To Hearing Aids
With new hearing aids your concept of “normal” hearing will need to be relearnt.
Read More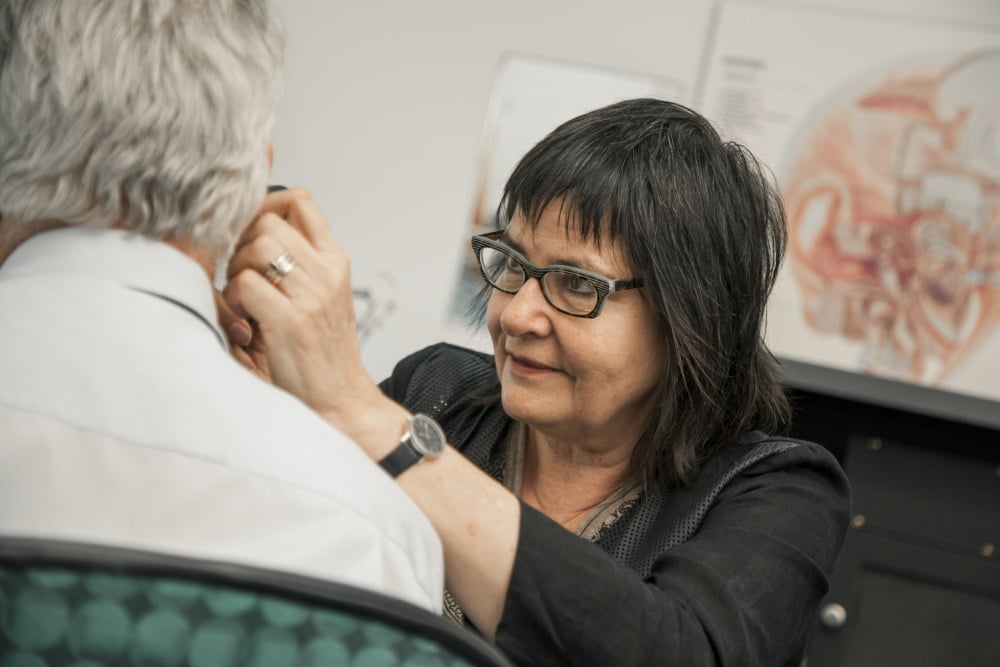
Fine-Tuning Hearing Aids
We have extensive training, experience and expertise in fine-tuning contemporary hearing aids to individual communication needs.
Read More
Hearing Aid Fittings
Your fitting package will include an instruction booklet and the accessories needed for maintenance and dehumidification
Read More
Hearing Aid Maintenance
To minimise the need for repairs and to preserve the life of your hearing aids, regular and thorough maintenance is essential.
Read More
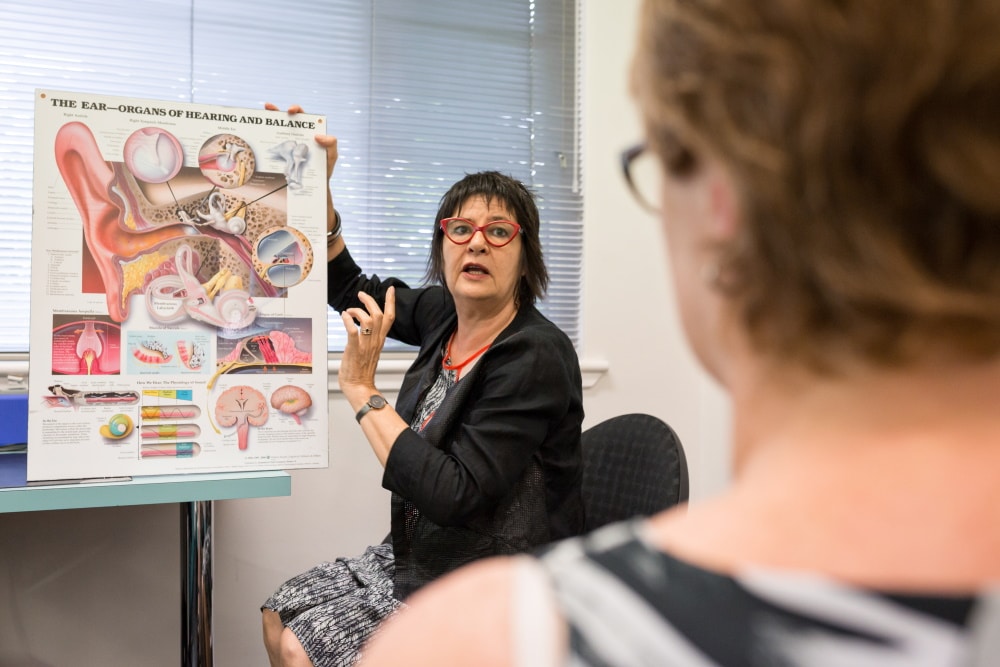

Hyperacusis & Misophonia
Both conditions have the potential to escalate, so that an increasing range of sounds become intolerable.
Read More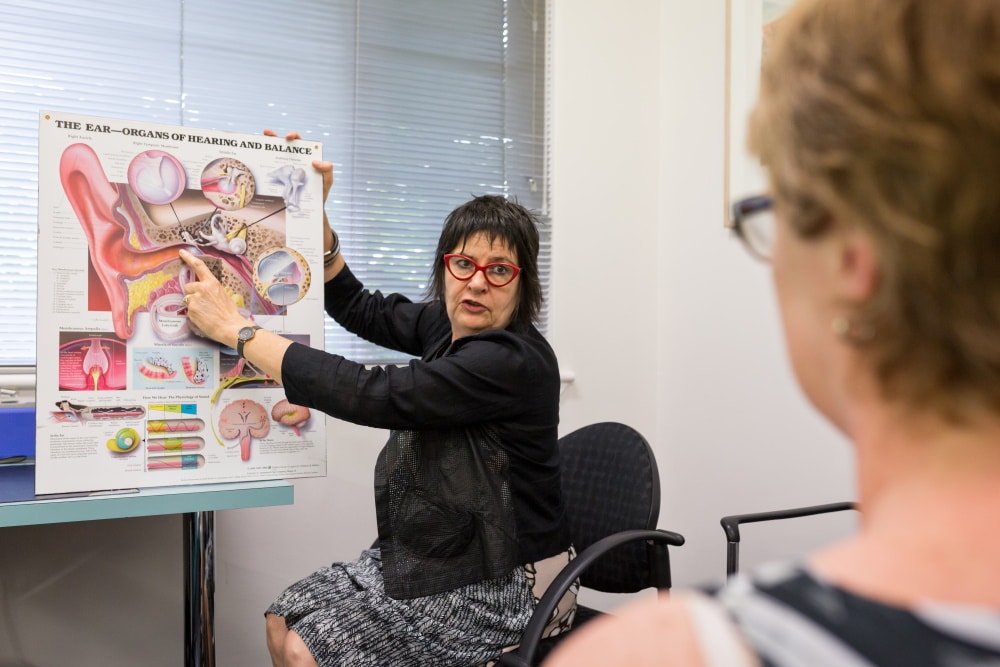

Misophonia
Misophonia is a strongly aversive response or abnormal sensitivity to certain specific sounds
Read More
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the term used to describe hearing any sounds which are not present externally.
Read More
Acoustic Shock
Acoustic shock is an involuntary fright/psychological trauma reaction to sudden, loud noises.
Read More
